About McStas
Conditions of use
Authors/Contacts
Project funding
Download
Components
Other Downloads (share)
Documentation
Wiki (GitHub)
McStas manual
Publications
November 29th, 2023: (experimental) McStas packages have hit conda-forge
Dear all,
Thanks to help from Thomas Kittelmann (ESS DMSC), McStas is now available on conda-forge
Initially we support only support Unix platforms Linux and macOS Intel, but macOS Silicon should come shortly.
The version tag of the packages is "3.4.7" meaning functionality-wise like McStas 3.4 but with minor improvements. For next official McStas release everything should match between our classical binary-distributed platforms and conda-forge.
Should you experience problems, please write up a GitHub Issue.
In preparation for forthcoming McStas 3.5 we are very much open to contributions:
Hence, if you have nice new component developments or new instrument
files to contribute, please fork the our repo and open a
pull request adding the files!
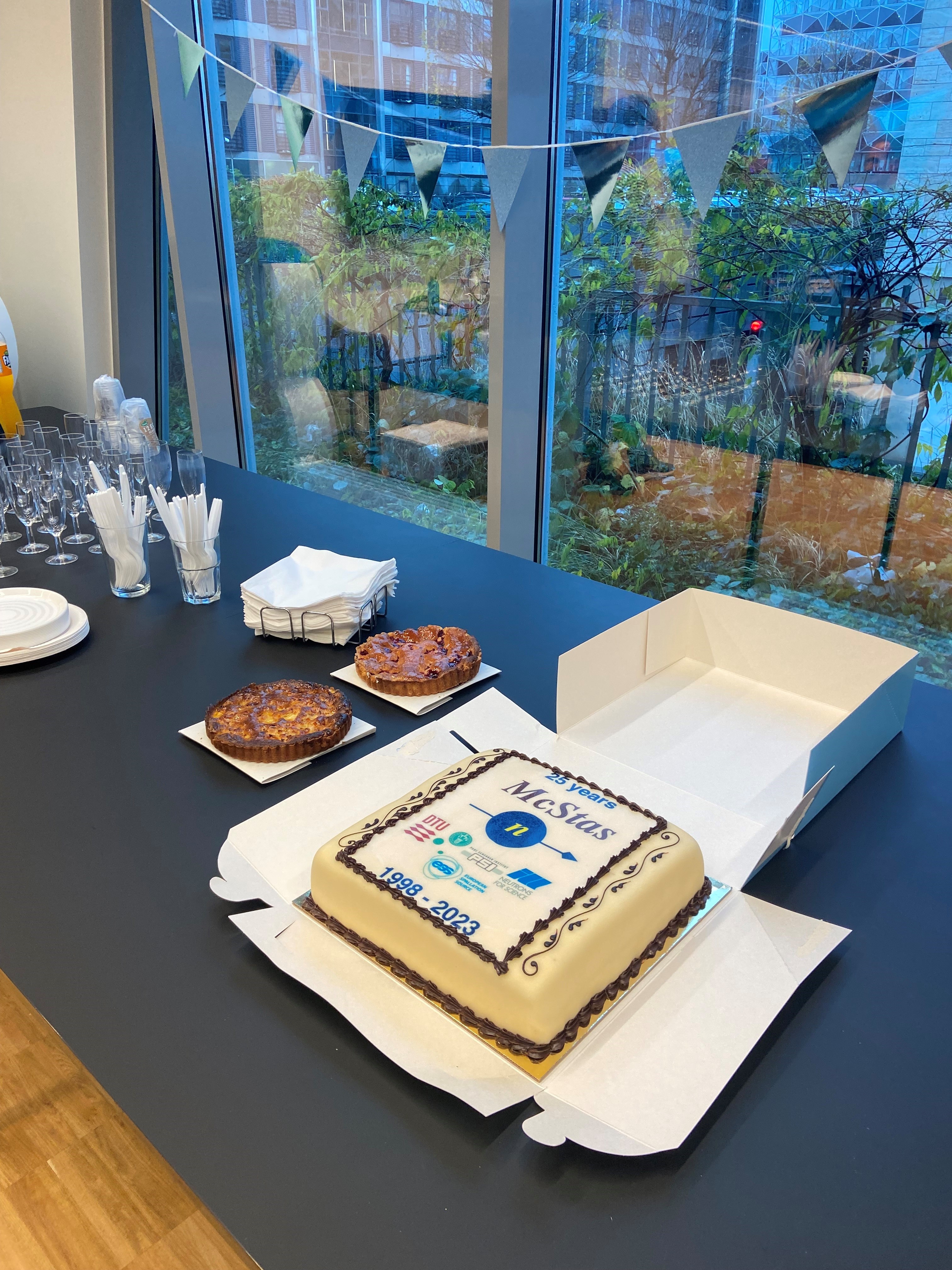
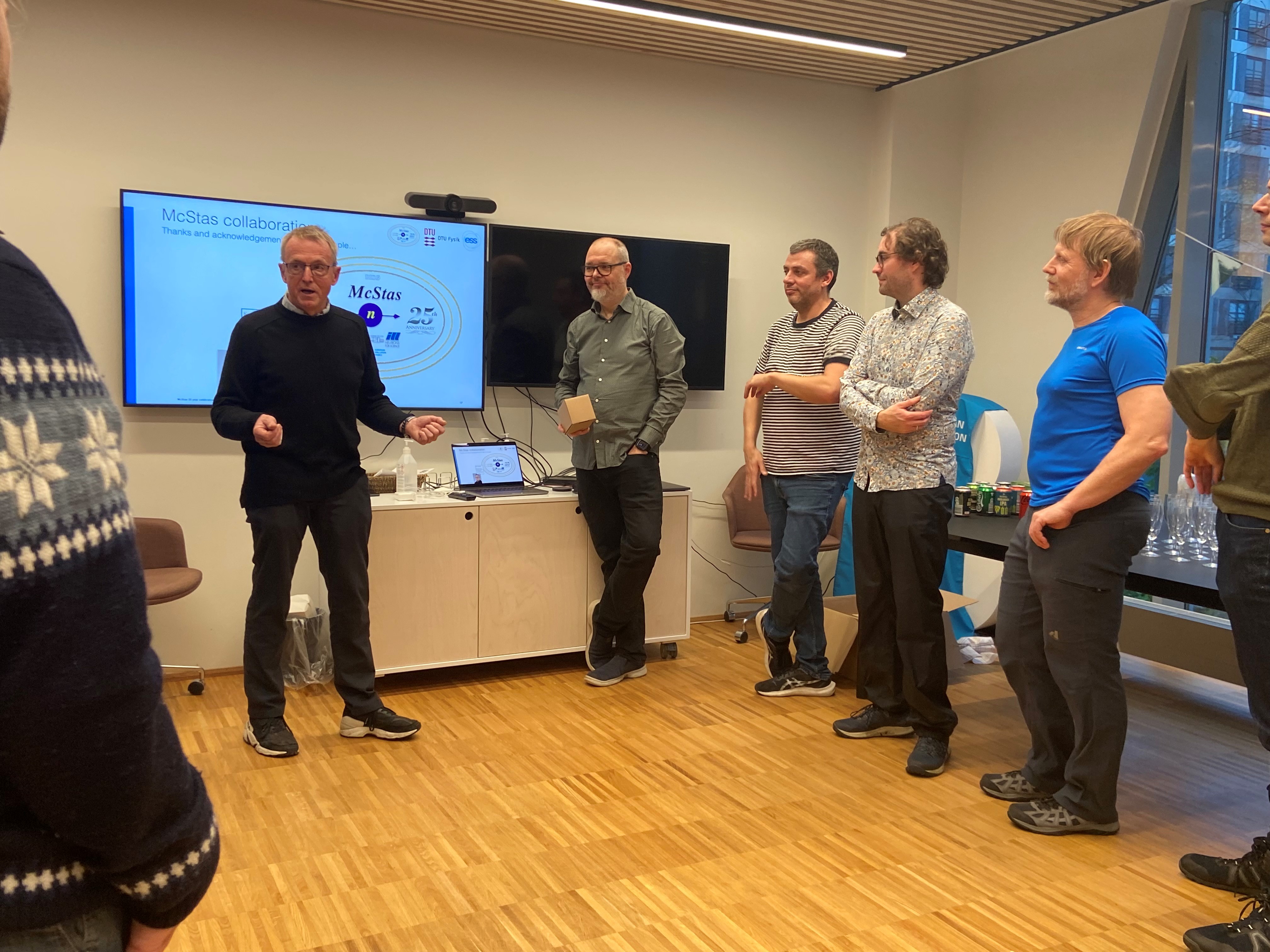
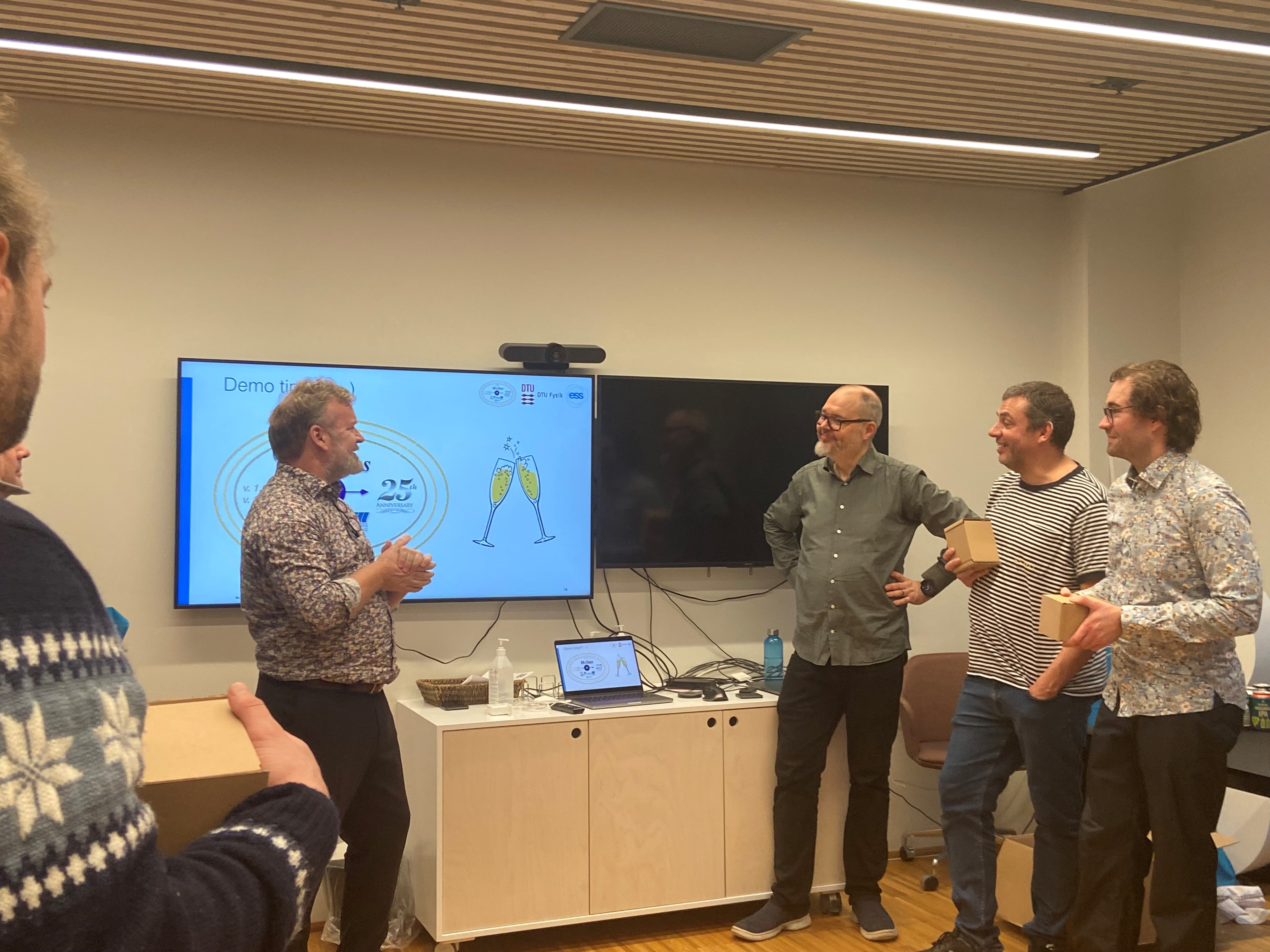
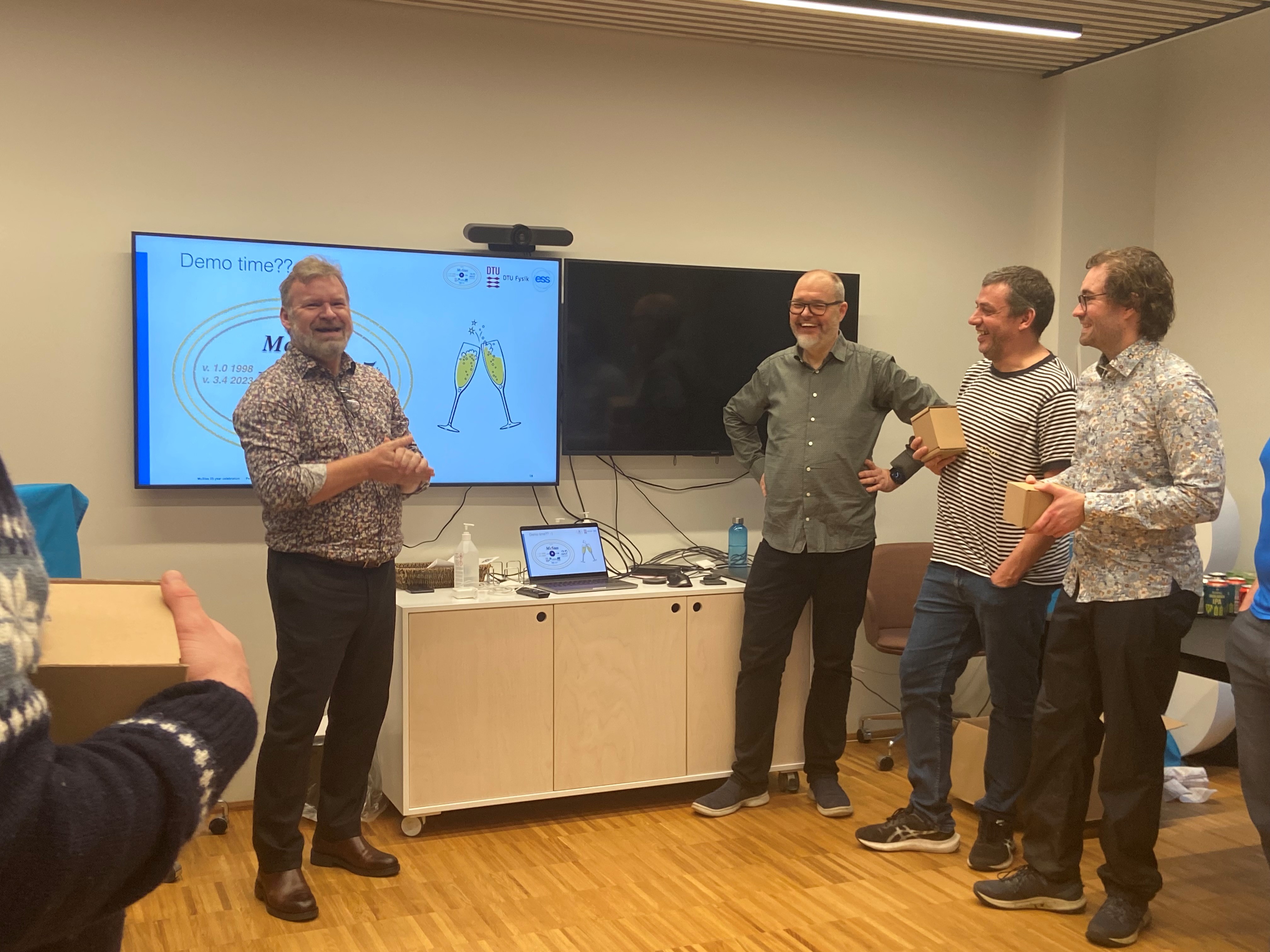
November 16th, 2023: The McStas project marks 25 year anniversary
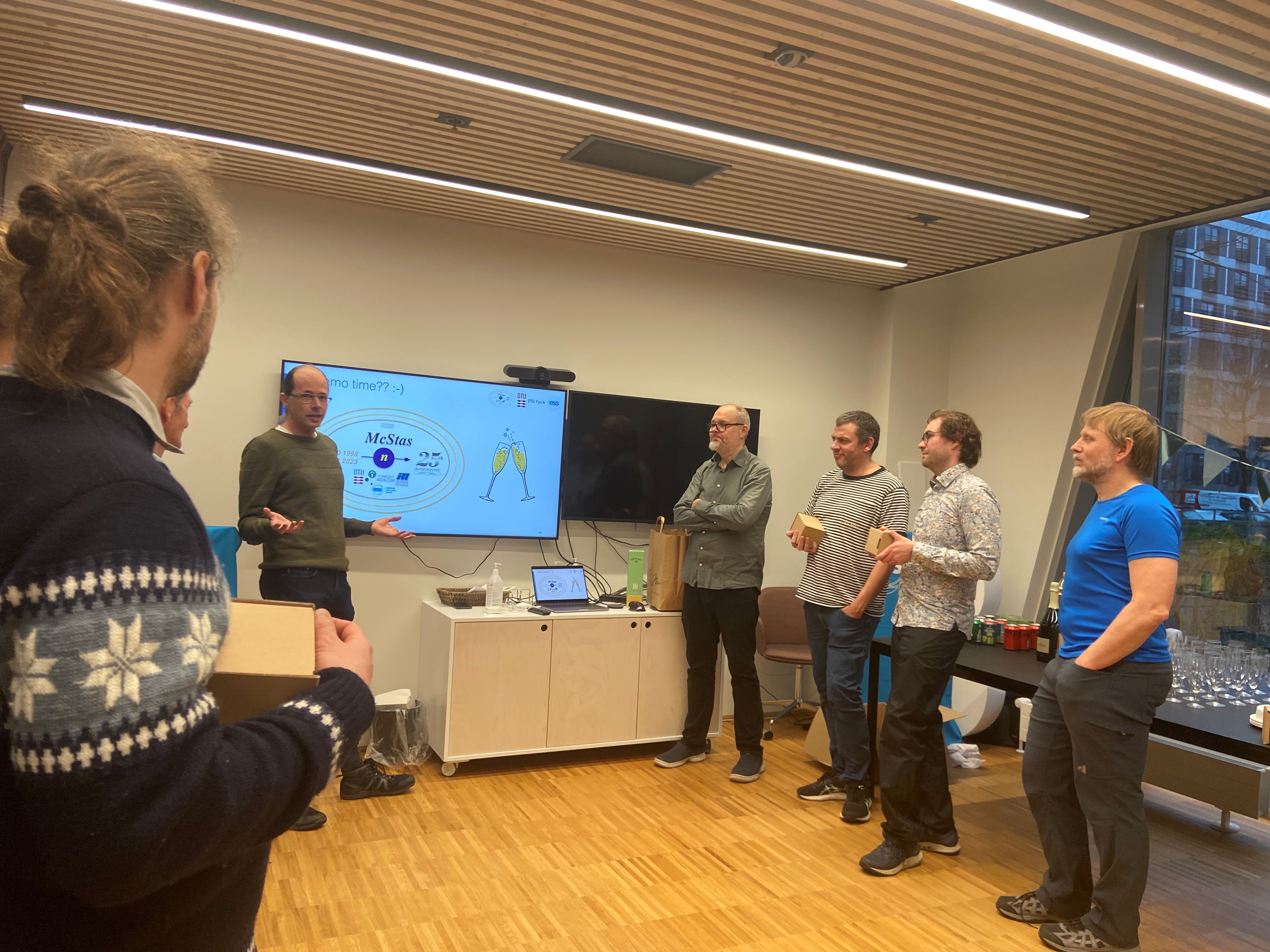
The 25th-anniversary celebration of the McStas collaboration took place on the afternoon of November 16th, co-hosted by ESS DMSC and DTU Physics.
Commencing its journey at Risø National Laboratory in the spring of 1997, the McStas software commemorated its 25th year since the release of version 1.0 in October 1998. Over the years, the project expanded into an international collaboration, with notable contributions from institutions such as Institut Laue-Langevin (ILL) and The Paul Scherrer Institute (PSI). In 2007, Risø became part of DTU, and since 2012, the ongoing development of McStas found a new home at DTU Physics, actively collaborating with the Niels Bohr Institute, ILL, PSI, and ESS.
As an open-source software, McStas has benefited from widespread contributions by individual researchers from facilities and universities globally, enriching the codebase with new features and functionality.
McStas has evolved into the leading software globally for neutron scattering simulations, particularly in the realms of instrument design, optimization, and virtual experiments. Notably, the software played a crucial role in designing and optimizing most of the ESS instruments currently under construction in Lund, Sweden.
During the anniversary event, Peter Willendrup, the lead developer and technical-scientific support for the McStas user community since 2002, provided a comprehensive overview of the 25-year development journey, highlighting key contributions from various contributors. Peter is Senior Research Engineer at DTU Physics and ESS DMSC. Mads Bertelsen, the author of McStasScript, guide_bot, and Union presented his work on these significant developments. Mads is recently appointed to a permanent position as Scientist at ESS DMSC.
Several event participants delivered short speeches in honor of the McStas collaboration, including Kurt Clausen, originator of the "simulation framework" idea and grant holder of the first EU funding for McStas, Kim Lefmann founder and member of the McStas team since the start , Kristian Nielsen, the computer scientist who engineered the initial code-generator technology, and Thomas Holm Rod, head of the ESS DMSC. Another important guest was Emmanuel Farhi from Synchrotron SOLEIL, long time contributor to McStas and now the lead on McXtrace.
Pictures from the celebration:
Also, thanks to the colleagues at ORNL who sent us a nice birthday card! :-)
And to José Robledo and Sunyoung Yoo who were behind this lovely greeting and handcraft :-)
November 1st, 2023: Hints to install McStasScript with McStas 3.4 on Linux
Dear all,
As you may have noticed, the McStas installers for Windows and macOS now come with McStasScript embedded.
To achieve the same functionality on Linux (e.g. Debian/Ubunutu), you should perform these few steps
pip install jupyterlab ipympl mcstasscript nodejs jupytext
(Please note any information on the location of your pip installation)- Find the file
configuration.yamlwithin your pip installation, e.g.:.local/lib/python3.10/site-packages/mcstasscript/configuration.yaml - Edit that file to achieve the content
other: characters_per_line: 85 paths: mcrun_path: /usr/bin mcstas_path: /usr/share/mcstas/3.4
Once these steps are performed you should be able to perform tasks like
- Use
mcstas-pygento generate a McStasScript.pyversion of an existing instrument:~> mcstas-pygen BNL_H8.instr Warning: 'V_sample' is an obsolete component (not maintained). !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! !!! WARNING: Your instrument file uses an input-parameter named !!! !!! "lambda" - which is a reserved word in Python !!! !!! As a workaround the variable has been named "Lambda" in !!! !!! the output python script. !!! !!! PLEASE consider renaming lambda->Lambda in the .instr file !!! !!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! CFLAGS=
- Use
jupytextto convert from.pyto.ipynbformat:~> jupytext --to ipynb BNL_H8_generated.py [jupytext] Reading BNL_H8_generated.py in format py [jupytext] Writing BNL_H8_generated.ipynb
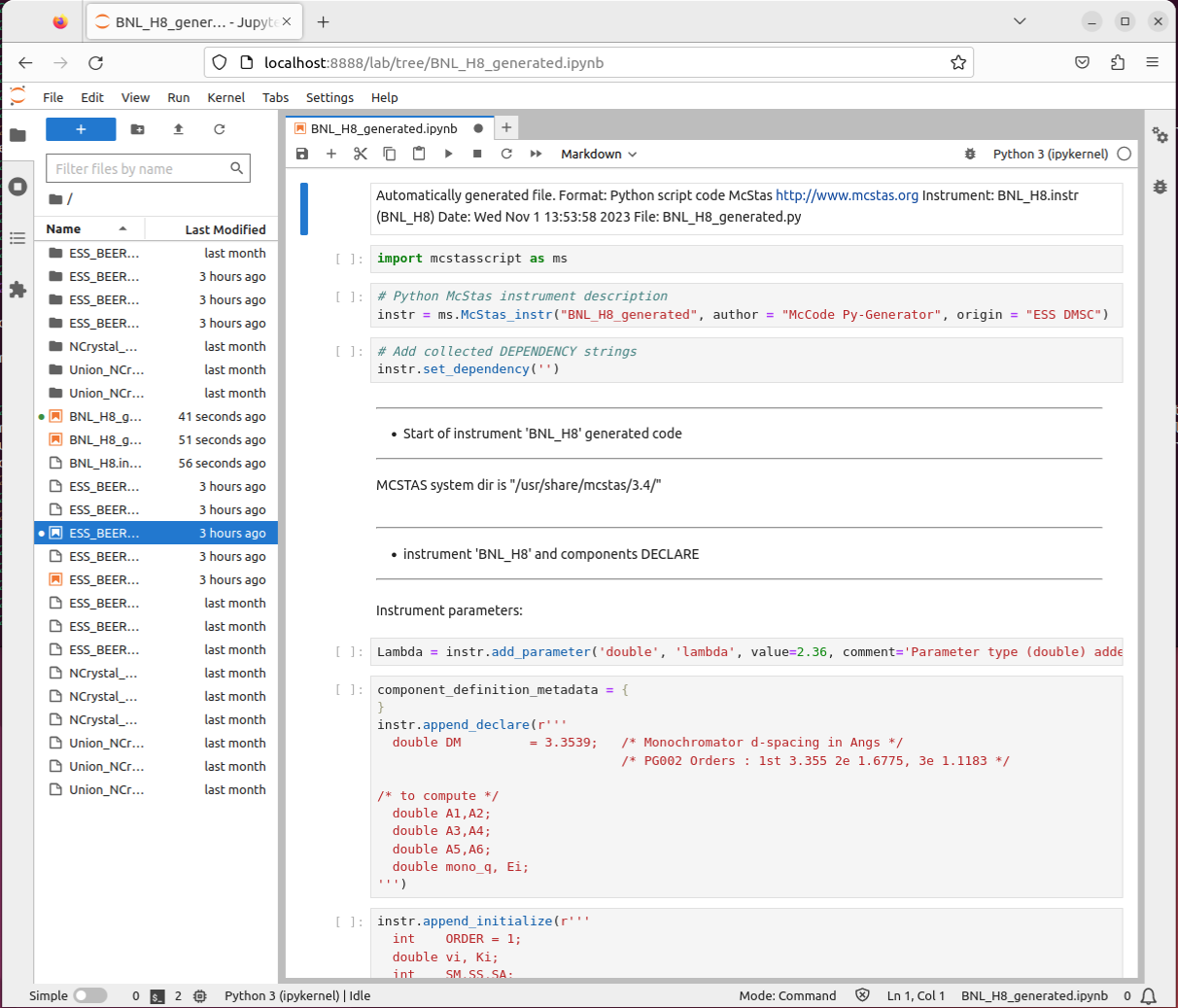
- Run
jupyter lab BNL_H8_generated.ipynbto interact with your converted instrument in Jypyter Lab. - This should start a jupyter server and bring up a browser:
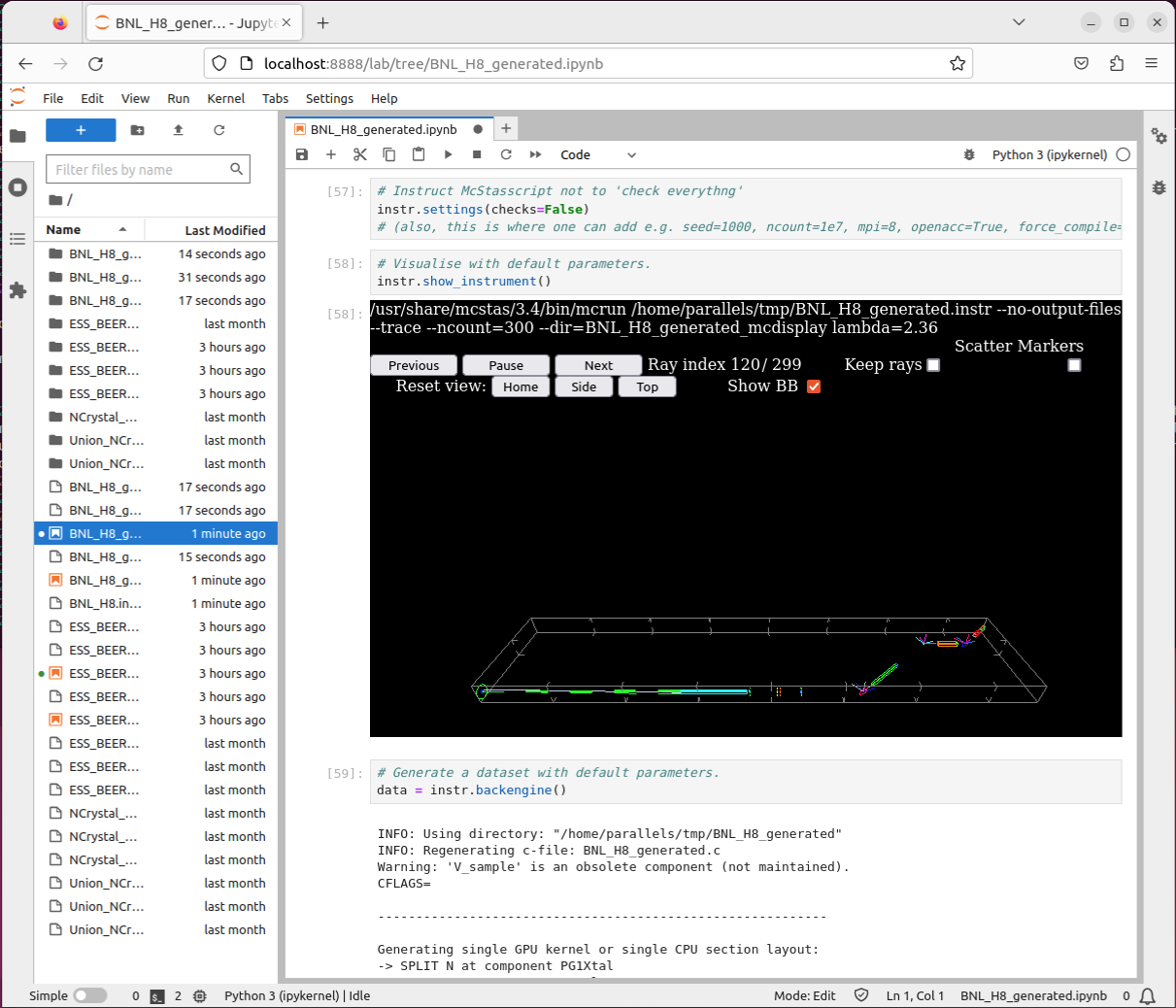
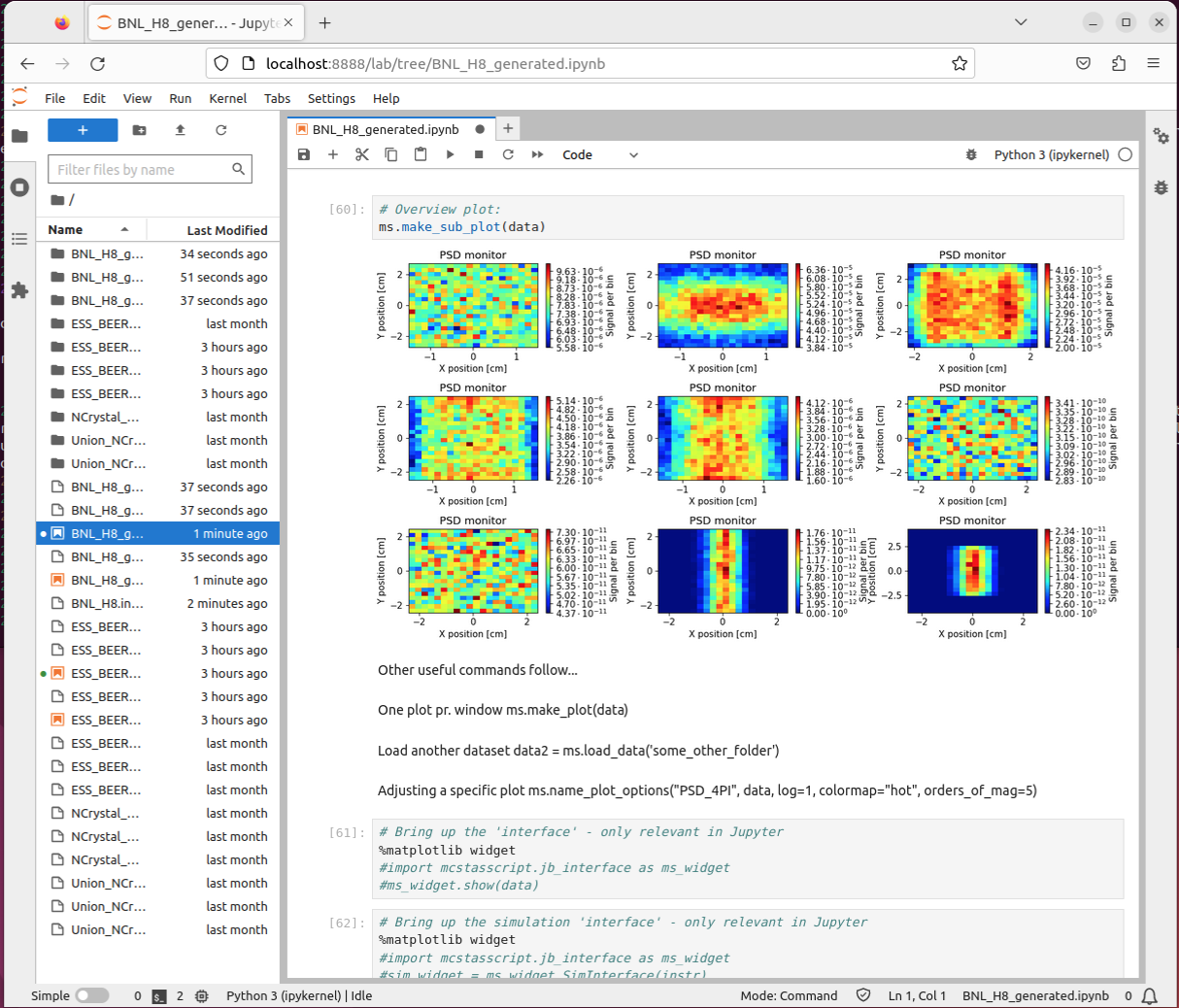
- Executing the cells should give you access to a rendering of the
instrument and some output simulation data:
September 23rd, 2023: McStas 3.4 Docker and Binder available
Dear all,
A Ubuntu 22.04 + McStas-3.4 + McStasScript image is now uploaded to dockerhub. To run from your local podman / Docker / etc. installation, execute a command along the lines of:
podman run -p 8888:8888 docker.io/mccode/mcstas-3.4
+ follow instructions from podman/Docker
You may also run the same container via binder, please connect via
this icon:
To start McStas, please issue the command mcgui from a terminal.
September 21st, 2023: McStas 3.4 linux 'meta-packages' respun
Dear all,
A minor hickup was found with our Debian/Fedora metapackages that
both had a dependence on mcstas-mcpl-3.4 which is a
non-existent package.
Newly built, corrected meta-packages have been uploaded as replacement, so please re-attempt installation if you experienced issues earlier.
Also, please be aware that mcpl and NCrystal now come
in separate, non-McStas related packages - and are not included in
the "metapackage" on Fedora. To install them, simply execute
sudo dnf install mcpl ncrystal
Sorry for any inconvenience caused!
September 19th, 2023: McStas 3.4 released
Dear all, The new McStas release v. 3.4 "next-generation" is built and ready for download!
McStas 3.4 is the fifth official release in the 3.x series, with a modernised code-generator and support for GPU acceleration on NVIDIA cards.
3.4 is a 'major' update with notable changes, e.g. tighter integration/interoperability with McStasScript, new grammar and further CMake-standardisation which will eventually bring McStas to the conda-forge ecosystem. (And todaay, almost all dependencies for McStas are brought by mamba/conda on macOS and Windows.) Thanks to Thomas Kittelmann (ESS) for lots of help and footwork!
Another notable change is that MCPL and NCrystal are now
distributed in stand-alone .deb / .rpm packages that are
McStas-release-independent, for convenience still available through the
packages.mccode.org repository. Please install using e.g.
apt install mcpl ncrystal
(The MCPL and NCrystal codes have been submitted to the
Debian ecosystem by Synchrotron SOLEIL / Emmanuel Farhi / Roland Mas
and should make it to the next Debian Stable, the same procedure is
also under way for McStas.)
Thanks:
Thanks to all members of the joint McStas-McXtrace team and input from our users via emails and GitHub issues alike!
Download and installation instructions are available via our GitHub INSTALL-doc pages.
Selected highlights from the releass are listed below. The full
list changes is also available at https://mcstas.org/CHANGES_McStas.
Dear all,
The new McStas release v. 3.3 "next-generation" is built and ready for download!
McStas 3.3 is the fourth official release in the 3.x series, with a modernised code-generator and support for GPU acceleration on NVIDIA cards.
3.3 could have been considered a 'minor' update, but new built-in
support for NeXus on all platforms and new Thanks:
Download and installation instructions are available via our GitHub INSTALL-doc pages.
Selected highlights from the releass are listed below. The full
list changes is also available at https://mcstas.org/CHANGES_McStas.
If you didn't start already, please start your migration to 3.x:
Fixes of issues from last 3.x release: Release highlights Our Docker and binder containers will be updated within the
following weeks.
We hope you will enjoy this new release!!!
Previous news items: 2022, 2021,2020,2019, 2018, 2017, 2016,
2015, 2014, 2013,
2012, 2011, 2010, 2009,
2008, 2007, 2006,
2005, 2004, 2003, 2002, 2001, 2000, 1999,
1998.
We hope you will enjoy this new release!!!
(!!! Please note that there will be no future
2.x releases !!!)
mcrun --help
in your McStas terminal to learn
about details of switches and parameters or see the the changelog
for a full description.
mcstas-pygen Instrument.instr generates the .py
script Instrument_generated.py
Using 'jupytext' this file may easily be converted to a notebook:
jupytext --to ipynb Instrument_generated.py
generates notebook file Instrument_generated.ipynb
See https://github.com/PaNOSC-ViNYL/McStasScript
and https://mads-bertelsen.github.io for more information on McStasScript.
DEFINE INSTRUMENT template(lambda / "Aa" =
2.36)
see the changelog
for full description.
METADATA grammar from Greg S. Tucker (ESS), can
be used to attach verbatim code/information to one or more
component instances. See the changelog
for full description.
March 31st, 2023: McStas 3.3 released
SEARCH grammar warrant the .x increment.
Thanks to all members of the joint McStas-McXtrace team and input from our users via emails and GitHub issues alike!
- If you are still in trouble, please write us a GitHub issue or an email to mcstas-users@mcstas.org
A number of issues from 3.2 were addressed, see the relevant GitHub issues for details:
3.2 issue list
mcrun now automatically adds NeXus support to your binary if --format=NeXus is given on the
commandline (or if DEPENDENCY " @NEXUSFLAGS@ " is
included in your instrument or component file).
--IDF will run an IDF generator (i.e. mcdisplay-mantid) prior to performing
a NeXus-based simulation, i.e. for "one-click" support of output in Mantid-compatible NeXus
format with an embedded IDF. Please consult the naming-conventions for sourceMantid, sampleMantid
and nD_Mantid_xx found in https://github.com/mccode-dev/McCode/wiki/McStas-and-Mantid#mcstas-mantid-workflow
to succesfully generate your IDF. Please also inspire from the example instruments in the Mantid
category, see mcgui -> File -> New from template -> Mantid .
mcrun now forwards the -I input to the code-generator, which allows you to add a chosen folder
with extra components etc. to your search path. Setting the -I flag implies recompilation (-c).
(Please also note the related SEARCH grammar below which allows working on the component search
path directly via the instrument or component grammar.)
mcgui run dialogue now allows to directly specify --format=NeXus and --format=NeXus --IDF when starting a simulation.
mcdisplay-mantid has been given a good overhaul and now works properly with all of the supported
mantid-event-detector geometries of Monitor_nD: rectangular, cylindrical/banana and OFF-file based.
Thanks to Torben R. Nielsen and Celine Durniak (ESS) for repeated testing.
mcplot (-pyqtgraph) and numpy related bug was quickly spotted
and ironed out with the help of by Rose Robledo FZJ.
FZP_simple model.comp of Fresnel Zone-Plate (phenomenologic/closed-form thin-plate approximation) added
along with test instrument Test_FZP_simple.instr, work by Anders Komar Ravn (NBI), and Erik B Knudsen
(previously DTU, now Copenhagen Atomics)
Test_Monochromators.instr has been updated to include NCrystal_sample as a monochromator, plus
includes multiple ways of parametrizing Single_crystal lattice
orientation. (Please note that NCrystal support is still not complete on Windows.)
ConicTracer interface-component codes Conics_EH.comp, Conics_PH.comp, Conics_PP.comp
have been updated to allow specifying non-equidistant radii of the nested optical shells. Please
use vector radii={a,b,c,d,e} or initialization via an instrument-based array and use a compatible
setting of nshells.
Elliptical_guide_gravity.comp will now complain if you are using arrays for specifying varied coating
without setting the nSegments input.
Pol_guide_vmirror.comp has been ported to 3.3.
Thanks to Damian Rodriguez and Hal Lee (ESS) for interactions on this component.
ESS_butterfly component may be modified using
compile-time re-definition. Defaults are
ESS_SOURCE_DURATION0=2.857e-3 s,
ESS_SOURCE_FREQUENCY 14 Hz,
ESS_SOURCE_POWER 5 MW. (Use e.g. mcrun --D1=ESS_SOURCE_DURATION=1.0e-3 to simulate a 1 ms pulse.)
pol-lib may also be redefined at compile-time,
defaults are: MCMAGNET_STACKSIZE=12,
mc_pol_angular_accuracy=(1.0*DEG2RAD) deg,
mc_pol_initial_timestep=1e-5 s.
SEARCH has been added to the grammar, allowing users to run append a directory
to the mcstas search path when looking for components. The syntax may be given in the
instrument- or component-header directly after a SHELL token and before the DEPENDENCY, DECLARE
tokens, available in two variants:
But you may also apply the same two SEARCH "/the/path/to/add/"
SEARCH SHELL "the_executable --and --some --options"
SEARCH forms in connection with a component instance in TRACE, e.g.:
TRACE
...
SEARCH SHELL "readout-config --show compdir"
COMPONENT readout = Readout(ring="RING", fen="FEN", tube="TUBE", a="left", b="right", ...)
AT (0, 0, 0) ABSOLUTE
...
(r-)interoff-lib.c family of codes have again received a couple of updates, thanks to McStas user
Richard Wagner (ILL).
NCrystal library version 3.5.1 from T. Kittelmann (ESS) and X.X. Cai (CSNS), distributed
with McStas on Unix platforms only. (Cross-compiles for Windows, but still needs work
for "production" availability.)
MCPL library from the same authors included at v. 1.6.1